Anhedonia is a complex and debilitating symptom that affects millions of people worldwide. Here, we’ll delve into the world of anhedonia, covering its definition, impact on mental health, different types, treatment options, and its connection to cannabis use.

What is Anhedonia?
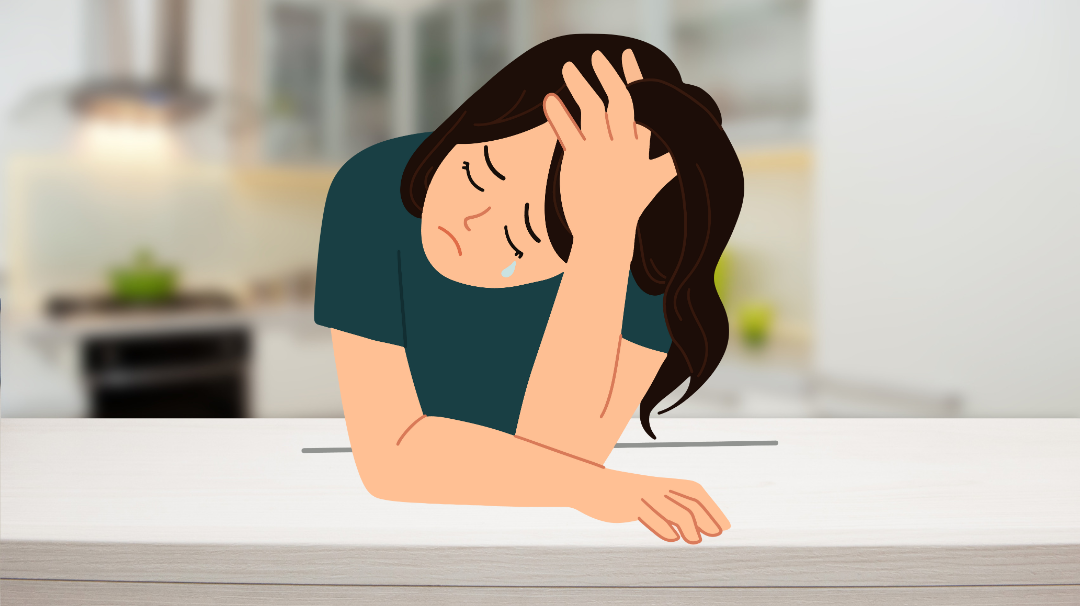
Anhedonia is a term derived from the Greek words “an” (without) and “hedone” (pleasure), which quite literally means “without pleasure”. It is a symptom characterized by an inability to experience pleasure from activities or stimuli that would typically be enjoyable.
Imagine not being able to find joy in activities that once brought happiness. For example, eating your favourite meal, engaging in hobbies, or spending time with loved ones just isn’t enjoyable anymore.
A recent study highlighted in PsyPost provides insight into anhedonia as an often overlooked but very common symptom of depression. They note that depression, a widely recognized mental health condition, often features anhedonia as one of its defining characteristics. In fact, anhedonia is one of the key diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder, making it an essential aspect of understanding and addressing depression.
Understanding the difference between anhedonia and apathy is crucial. Apathy is a lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern, whereas anhedonia is specifically the inability to experience pleasure. However, apathy may be a symptom of anhedonia.

Who is Impacted?
Anhedonia is not limited to those with depression alone; it can also be associated with other mental health conditions and illnesses. The impact of anhedonia extends beyond depression to conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and substance use disorders.
For those suffering from depression, anhedonia can be particularly crippling. It can make it challenging to derive pleasure from everyday life, leading to a diminished quality of life. Moreover, the presence of anhedonia can often predict the severity and course of depressive episodes, making it a critical marker for clinicians to consider during assessment and treatment planning.

Different Types of Anhedonia
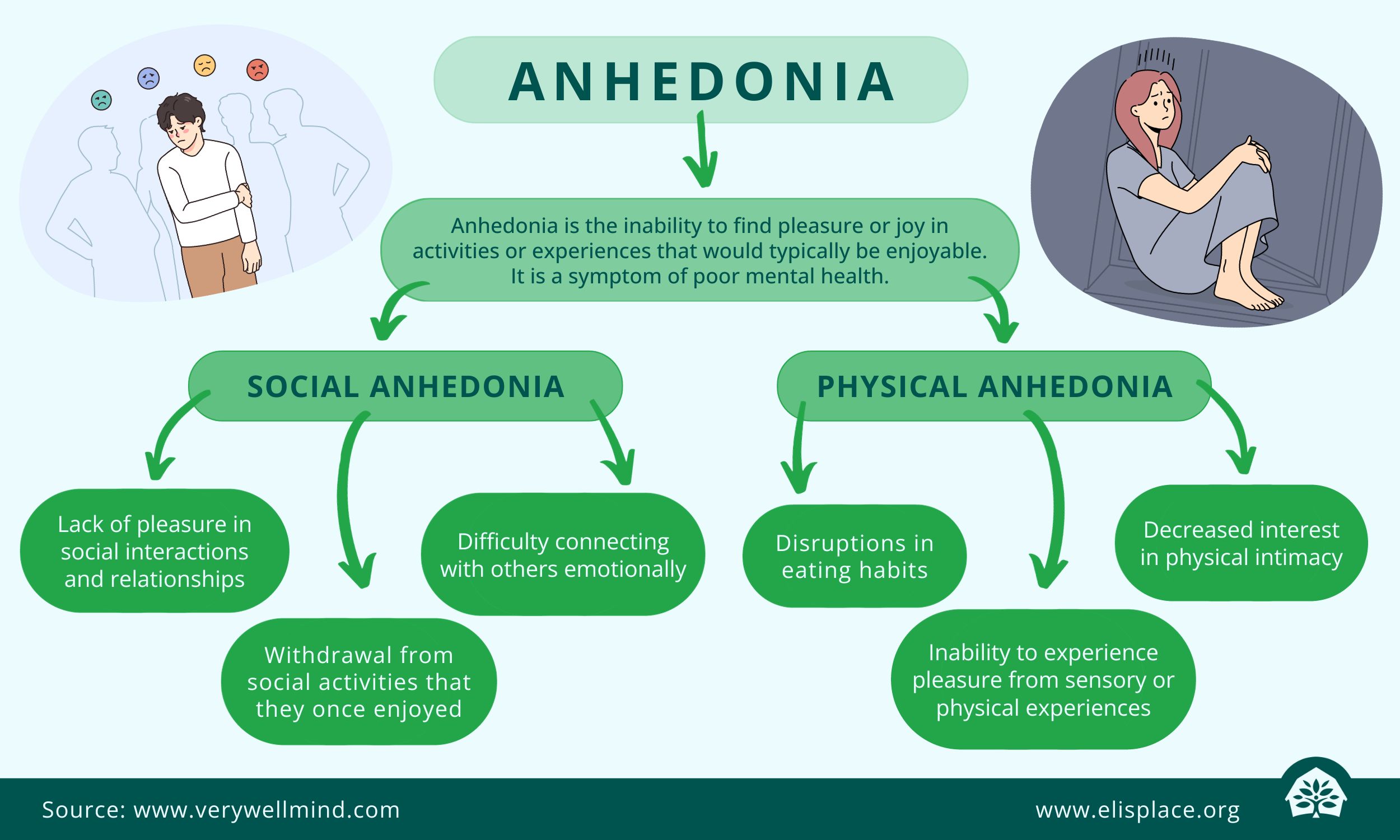
Anhedonia isn’t a one-size-fits-all symptom; it comes in various forms. Two primary types of anhedonia are:
- Social Anhedonia: This type is characterized by a lack of pleasure in social interactions and relationships. Individuals with social anhedonia may find it difficult to connect with others emotionally and may withdraw from social activities that they once enjoyed.
- Physical Anhedonia: Physical anhedonia is the inability to experience pleasure from sensory or physical experiences, such as eating, touching, or listening to music. This can lead to disruptions in eating habits, decreased interest in physical intimacy, and overall reduced engagement with sensory experiences.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for tailoring effective treatment strategies.

How is it Treated?
Anhedonia can be a challenging symptom to treat, but there are several approaches that individuals, in consultation with mental health professionals, can consider:
- Medications: Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and atypical antidepressants, may be prescribed to alleviate anhedonia in cases of depression or other mood disorders. These medications work to balance neurotransmitters in the brain to improve mood and increase the ability to experience pleasure.
- Therapies: Psychotherapy, particularly cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) and behavioural activation therapy, can be beneficial in addressing anhedonia. These therapies help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviours that contribute to anhedonia.
- Newer Options: There are emerging treatments like electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), ketamine therapy, and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). These therapies target anhedonia and other depressive symptoms through different mechanisms. ECT involves controlled seizures to reset brain chemistry, while ketamine and TMS are designed to modulate brain activity to alleviate depression.
It’s crucial to remember that treatment plans should be tailored to each individual’s unique needs and the underlying cause of anhedonia.

The Connection Between Cannabis Use and Anhedonia
An interesting area of study in recent years is the potential link between cannabis use and anhedonia. While many people use cannabis recreationally to experience pleasure, chronic cannabis use may lead to a phenomenon known as cannabis-induced anhedonia.
Cannabis contains compounds like tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) that interact with the brain’s reward system. Initially, this can lead to feelings of euphoria and pleasure. However, with frequent use, the brain’s reward system may become desensitized, leading to a reduced ability to experience pleasure from other natural rewards, such as food or social interactions. This condition is referred to as cannabis-induced anhedonia.
It’s important to recognize that not everyone who uses cannabis will experience anhedonia, and individual responses can vary. Furthermore, research into this area is ongoing, and more studies are needed to fully understand the relationship between cannabis use and anhedonia.
Anhedonia is a complex symptom that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, especially when associated with conditions such as depression. It’s important to recognize anhedonia as a distinct symptom, understand its various forms, and consider tailored treatment options.
Additionally, ongoing research into its connections with substances like cannabis can provide valuable insights into how anhedonia can manifest in different contexts. If you or someone you know is experiencing anhedonia or related symptoms, seeking professional help and support is essential on the journey toward mental well-being.
Eli’s Place will be a rural, residential treatment program for young adults with serious mental illness. To learn more about our mission and our proven-effective model click here.