Sleep, as it is interwoven with mental illness, health and well-being, is often underestimated. Yet, delving into the complex interplay between sleep and mental health reveals a deep relationship, one vital for holistic wellness.
Sleep refers to the state of rest in which our bodies and minds rejuvenate and within that state, there are a variety of stages of sleep with specific impacts on the mind and body.
The connection between positive mental health — which encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being — and sleep is well documented. To discover more information on the link between mental health and sleep, you can revisit an earlier blog on the topic of sleep which discusses the importance of sleep in maintaining mental health.
In this article, our focus shifts to exploring the relationship between sleep and mental illness. Distinct from mental health, mental illness refers to conditions (often chronic conditions) that affect a person’s thinking, feelings, mood, or behaviour. These symptoms can profoundly impact one’s daily life in terms of relationships, work and the ability to complete the tasks of daily life.
Poor sleep can worsen the symptoms of existing mental disorders and may be a contributing factor to the development of new ones. Therefore, it is important to recognize the profound impact of sleep on psychiatric conditions.

Sleep Impacts Everyone
The quality and quantity of sleep can affect people differently, but their importance remains universal. Poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep duration can lead to several health issues, including impaired cognitive function, decreased productivity, and elevated stress levels. Moreover, disrupted sleep patterns can aggravate existing mental health conditions or even contribute to the onset of certain disorders.
Numerous studies have established a clear correlation between quality sleep and better mental health outcomes. Research has linked adequate sleep to improved mood regulation, enhanced emotional resilience, and better stress management. Conversely, sleep deprivation or disturbances can increase the risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder.

Basic Science Behind Sleep & Brain
The fascinating science behind sleep and its impact on the brain is complex. During sleep, the brain undergoes essential processes, including memory consolidation, neural repair, and toxin removal. Disruptions to these processes due to inadequate sleep can compromise cognitive function and emotional regulation, contributing to mental health challenges.

Canadian Data on Sleep
In Canada, studies have shed light on the prevalence of sleep disorders and their implications for mental health. According to recent data, a significant portion of the population experiences sleep disturbances, with implications ranging from decreased productivity to heightened risk of mental illness. Studies suggest that only 77% of Canadians meet sleep duration recommendations. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for implementing targeted interventions and support systems.

How Lack of Sleep Impacts the Brain
The repercussions of inadequate sleep extend far beyond mere fatigue. Chronic sleep deprivation can disrupt neural pathways involved in mood regulation, emotional processing, and stress response. As a result, individuals may experience heightened irritability, impaired decision-making, and increased susceptibility to mental health disorders. Periods of poor sleep can create a negative feedback loop impacting both mental health and sleep. In particular, poor sleep can impact emotional reactivity and an increase in negative behaviours and suicidal ideation.
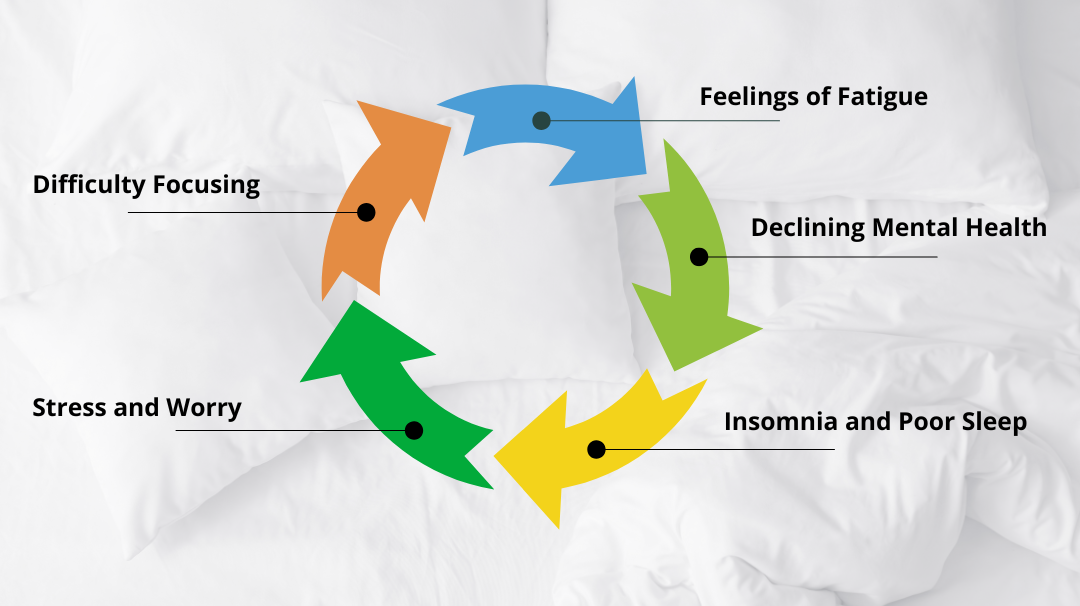

Impact on Mental Illness and the Understanding of the “Bi-directional” Concept
Experts commonly describe the relationship between sleep and mental illness as bi-directional, meaning that sleep disturbances can both precede and result from psychiatric conditions. For instance, individuals with untreated mental health disorders may experience disruptions in sleep patterns, exacerbating their symptoms. Conversely, chronic sleep deprivation or insomnia can increase the risk of developing mental illness or worsen existing conditions.
A recent study analyzed data from 89, 205 participants who wore wrist accelerometers tracking body movement for seven days. Using computational algorithms, including machine learning, researchers summarized the data into ten metrics, comparing sleep patterns between those with and without a history of mental illness diagnoses. CAMH psychiatrist Dr. Michael Mak highlighted the prevalence of sleep disturbances in mental health disorders, stressing the potential for improving mental health outcomes through treatments targeting sleep quality:
“We know that sleep disturbances cause a great burden to society, including an economic one. And we know that treatments that improve sleep quality, whether it is therapy or some types of medication, can improve mental health outcomes.” – Dr. Mak

Sleep and Mental Illness: An Overview
Sleep & Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is characterized by fluctuations in mood, energy levels, and activity patterns. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or hypersomnia (excessive sleep), are common among individuals with bipolar disorder and can significantly impact the course of the illness. Proper sleep hygiene and targeted interventions play a crucial role in managing bipolar symptoms and stabilizing mood fluctuations.
Sleep & Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex mental illness marked by disturbances in perception, cognition, and behaviour. Sleep abnormalities, including altered sleep patterns, obstructive sleep apnea, and reduced REM sleep are closely linked with schizophrenia. Symptoms of schizophrenia such as disorganized thoughts, hallucinations and changes in mood can be worsened by poor sleep. Addressing sleep disturbances through medication management and behavioural interventions can improve overall functioning and quality of life for individuals with schizophrenia.
Sleep & Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is characterized by emotional dysregulation, unstable relationships, and impulsive behaviour. Sleep disturbances, such as nightmares or night terrors, are prevalent among individuals with BPD and can exacerbate their symptoms. Incorporating sleep-focused therapies, such as Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I), into treatment plans can help alleviate sleep-related issues in individuals with BPD.
Sleep & Treatment-Resistant Depression
Treatment-resistant depression poses significant challenges for individuals and mental health professionals alike. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or hypersomnia, are common features of treatment-resistant depression and can hinder recovery efforts.

Conclusion
Addressing sleep disturbances as part of a comprehensive treatment approach, including medication management and psychotherapy, is essential for improving outcomes in individuals with treatment-resistant depression.
The relationship between sleep and mental illness is multifaceted and profound. By understanding the intricate connections between sleep and various mental illnesses, we can develop more effective strategies for prevention, intervention, and treatment. Prioritizing sleep hygiene and implementing targeted interventions can significantly improve outcomes for individuals living with mental illness. Understanding the crucial link between sleep and mental well-being is important for everyone; for those living with mental illness, ensuring quality of sleep is a critical aspect of any treatment plan.
Eli’s Place will be a rural, residential treatment program for young adults with serious mental illness. To learn more about our mission and our proven-effective model click here.




